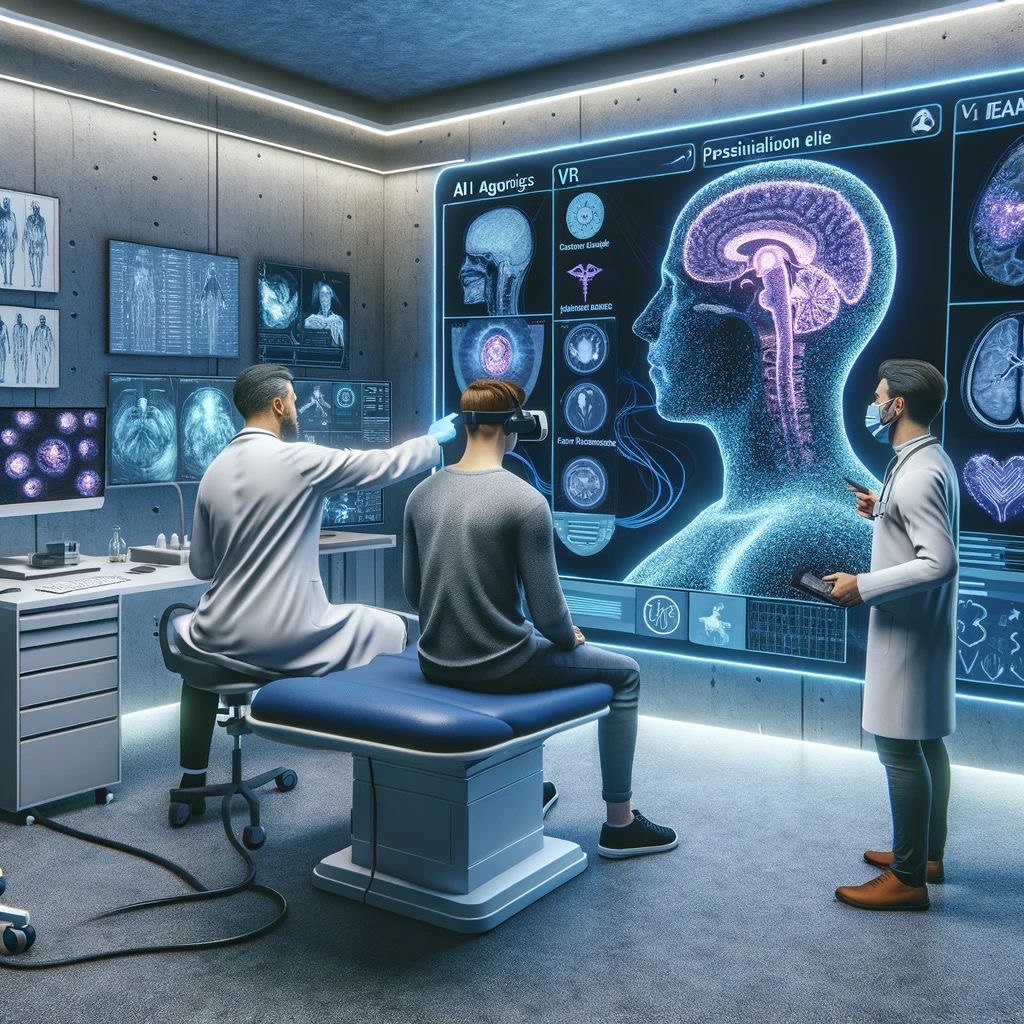
In recent years, the advent of artificial intelligence (AI) technology has revolutionized numerous industries. Many developed countries around the globe have tapped into these benefits, and Africa should not be left out. Africa is a continent of untapped potential and rich diversity. Healthcare is no different. However, African scientists are often hindered by limited resources. Within the context of Africa, where healthcare systems grapple with challenges such as inadequate infrastructure and limited access to medical expertise, AI can offer substantial opportunities. By leveraging machine learning and predictive analytics, healthcare practitioners can enhance diagnosis, personalize treatment plans, and optimize resource allocation, ultimately improving patient outcomes. In diagnostics, one of the key benefits of AI is the enhanced accuracy and speed of the diagnostic process. Traditional diagnostic methods rely heavily on the expertise and experience of healthcare professionals
In recent years, the advent of artificial intelligence (AI) technology has revolutionized numerous industries. Many developed countries around the globe have tapped into these benefits, and Africa should not be left out. Africa is a continent of untapped potential and rich diversity. Healthcare is no different. However, African scientists are often hindered by limited resources. Within the context of Africa, where healthcare systems grapple with challenges such as inadequate infrastructure and limited access to medical expertise, AI can offer substantial opportunities. By leveraging machine learning and predictive analytics, healthcare practitioners can enhance diagnosis, personalize treatment plans, and optimize resource allocation, ultimately improving patient outcomes. In diagnostics, one of the key benefits of AI is the enhanced accuracy and speed of the diagnostic process. Traditional diagnostic methods rely heavily on the expertise and experience of healthcare professionals
However, human analysis is not immune to errors, and misdiagnosis can severely affect patients. This is where AI comes in, beyond accurate diagnostics, AI-powered systems can also play a crucial role in optimizing treatment plans. By analyzing patient data and comparing it to vast databases of medical research and clinical trials, these systems can provide physicians with evidence-based recommendations for treatment. With the aid of AI, personalized treatment plans can be enhanced by analyzing large datasets of patient information, including medical history, genetic data, and diagnostic test results, to identify patterns and predict individual patient outcomes. In African healthcare settings, where access to specialized medical expertise is limited, AI can assist healthcare providers in making informed decisions about personalized treatment plans based on data-driven insights.
AI
Despite these benefits, the adoption of AI in healthcare
is not without its risks and ethical considerations. Issues such as data
privacy, algorithmic bias, and equitable access to AI-driven healthcare
solutions must be carefully navigated. In
To realize the full potential of AI in African healthcare,
concerted efforts are needed to overcome existing challenges. This includes
investment in infrastructure and technology,
Conflict Of Interest
The views and opinions expressed in this article are those of the author, and they do not purport to reflect the policies, opinions, or views of the AfroScience Network platform.
Disclaimer
This article has not been submitted, published or featured in any formal publications, including books, journals, newspapers, magazines or websites.
Be the first to comment
Please login to comment